Monofacial modules solely harness energy from the front side of the solar panels, whereas bifacial modules are designed to capture light on both the front and back surfaces, enhancing their efficiency.
This article will teach you more about bifacial solar panels, including their benefits, drawbacks, and efficiency.
What Are Bifacial Solar Panels?
Bifacial solar panels are equipped with solar cells on both their front and rear surfaces. This dual-sided design enables the collection of solar energy from the back of the panel, amplifying the overall energy yield. Owing to their capacity to harness sunlight from both directions, bifacial panels exhibit enhanced efficiency. Typically devoid of frames and metal gridlines, their transparent construction not only bolsters their structural integrity but also enhances their aesthetic appeal.
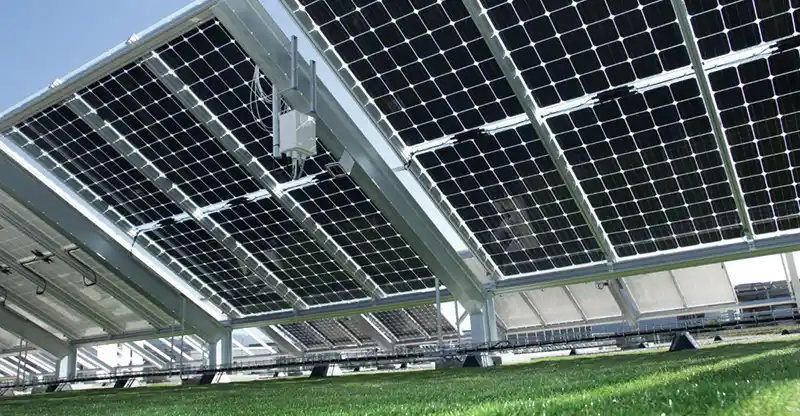

Bifacial Solar Panel VS Traditional Solar Panel
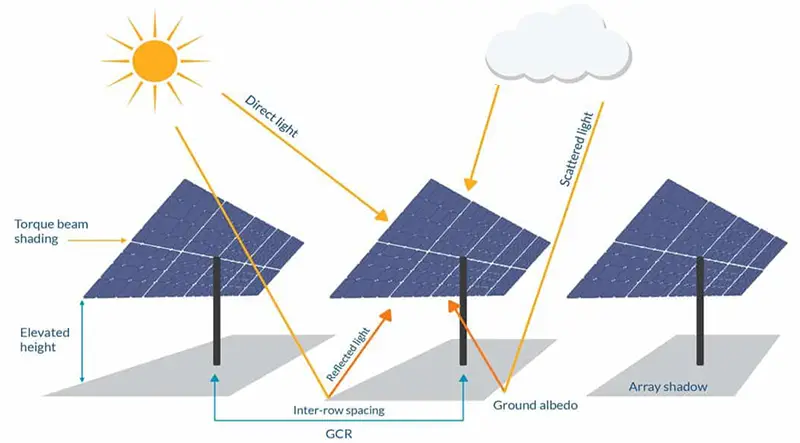
Bifacial solar panels are designed with solar cells situated between two layers of glass, allowing them to harness sunlight from both their front and rear surfaces. This configuration amplifies their energy output, particularly when placed atop white concrete surfaces. Typically employed in commercial or utility-scale settings, these panels are often raised and slanted from their mounting points, capitalizing on light reflections onto the rear side. Consequently, bifacial panels can capture light bouncing off the ground or other surfaces. In contrast, conventional solar panels feature a white backsheet, rendering them incapable of absorbing this reflected light. Therefore, in specific scenarios such as ground-mounted systems or rooftop installations, bifacial solar panels can offer distinct advantages.

How Much More Efficient is a Bifacial Solar Array?
In evaluating the optimal use of bifacial solar panels, several pivotal factors warrant attention to ensure peak energy yield.
Firstly, the reflectivity of the immediate environment plays a crucial role in the panels’ energy generation. Environments with lighter hues, such as areas with significant snow cover, enhance the light reflection, thereby augmenting the panels’ output.
Secondly, adequate spacing is imperative to allow reflected light to illuminate the rear side of the panels. Consequently, rooftops, where panels are closely aligned with shingles, may not be the most suitable locations for bifacials. Instead, these panels are best suited for expansive commercial setups where they can be elevated on poles, permitting ample light reflection from the rear.
A 2018 research by LONGi Solar indicated that bifacial panels could outperform traditional solar systems by 11% in efficiency. Incorporating a solar tracking mechanism, which constantly adjusts the orientation of solar cells to the sun’s path, can further enhance the efficiency of bifacial cells by up to 27%. However, the precise energy gain largely depends on the specific environmental conditions surrounding the installation.
Pros & Cons of Bifacial Solar Panels
Bifacial solar panels are gaining prominence due to their cost-effectiveness and superior efficiency. As more households and enterprises gravitate towards bifacial over monofacial panels, one must ask: do the advantages genuinely surpass the potential disadvantages?
The Advantages of Bifacial Solar Panels
● Increased Efficiency: Bifacial modules have the advantage of generating power from both surfaces, enhancing overall energy production.
● Enhanced Durability: Owing to their frameless design and the protection of tempered glass on both sides, bifacial panels often boast greater durability. The tempered glass offers resistance to weather elements, UV radiation, extreme temperatures, and forceful winds. Consequently, the robustness of these panels suggests a more extended lifespan.
● Aesthetic Appeal: Bifacial modules come in diverse designs, with many favoring the frameless variants. The sheer glass design is often regarded as more visually pleasing compared to the traditional monofacial panels.
● Superior Performance in Diffused Light: The augmented surface area of bifacial panels ensures better performance under diffuse light conditions, leading to reduced long-term costs compared to monofacial alternatives.
● Minimized Potential-Induced Degradation (PID): Frameless bifacial panels reduce the risk of potential-induced degradation, a phenomenon where electrical currents stray from their intended routes, leading to panel corrosion. Moreover, the absence of exterior metal contacts means that these bifacial panels don’t necessitate grounding.
● Extended Warranties: Many bifacial solar panels come with warranties that last up to 30 years.
The Disadvantages of Bifacial Solar Panels
The primary drawback of bifacial solar panels is their elevated cost. They tend to be marginally more expensive than their monofacial counterparts. Additionally, owing to their increased weight and the need for specialized equipment to maximize their advantages, the installation expenses are also higher.
The substantial cost discrepancy stems from the unique solar racking essential for bifacial panels.
To ensure minimal shading behind the bifacial solar panels, specialized racking is employed to hinder light from traversing the panels. This particular racking system is costlier and necessitates skilled installers for precise setup. Consequently, these factors contribute to the overall increased cost of installing bifacial solar systems.
Final Words
Bifacial modules are best suited for sites that can capitalize on the benefits of bifacial gain. Thus, homeowners with rooftop installations should consider alternative solar panel options. Given the optimal circumstances, bifacial modules can yield greater power with fewer components, optimizing both the initial expenditure and the subsequent return on investment.







